What is a PBX?
PBX stands for Private Branch Exchange, which is a private telephone network system used in company. Users can communicate with each other via extensions and share outbound line for making external calls. For example: long distances…
Benefits of PBX
Cost effective
Run on existing network
Easy to scalable and more
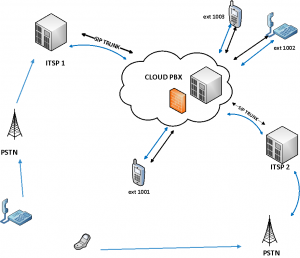
Requirement:
Software: Deploy Voip system PBX in a flash on VPS using Linux OS ex: CentOS, Ubuntu or using distro FreePBX available.
Hardware: 4 Xeon vCPUs, 3GB RAM, 40 GB SSD hard drives, 100mbps network connection, Ubuntu 14.04 LTS x64, higher is better performance.
Processing Steps:
- Create extensions:
- Using sip protocol, IAX
- Ext 1001, 1002, 1003…
- Trunking with ITSP
- Communicate between PBX to ITSP (Internet Telephony Service Provider)
- Create inbound traffic
- Traffic from ITSP goes to IVR, Ext, or Conference…
- Create outbound traffic
- Setup rules dial pattern, area code allowed go through ITSP
- Setup DID number
- Buy DID from ITSP callcentric, didx, voip.ms…
- Security:
- CSF (ConfigServer Security&Firewall) on webmin
- Allow IPs: allow access client connect to Voice Server
- Deny IPs: block unwanted client want to connect Voice Server
- SSH protection: changing default port 22 to others, banner protection
- Fail2ban: unwanted will be blocked after 3-5 attempted
- Control Panel:
- Webmin, monitor system, setup cronjob